Heart surgery is a critical medical procedure aimed at addressing various heart conditions and diseases. This guide provides an overview of heart surgery, including its types, reasons for undergoing surgery, the process involved, risks, recovery, and tips for patients and their families. Understanding what to expect can help alleviate anxiety and ensure a smoother experience.
Understanding Heart Surgery
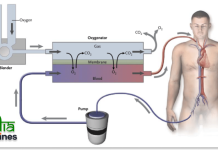
Heart surgery involves operations performed on the heart or blood vessels to correct problems. These procedures are typically carried out by cardiothoracic surgeons and can range from minimally invasive techniques to open-heart surgery.
Reasons for Heart Surgery
Heart surgery may be necessary for a variety of reasons, including:
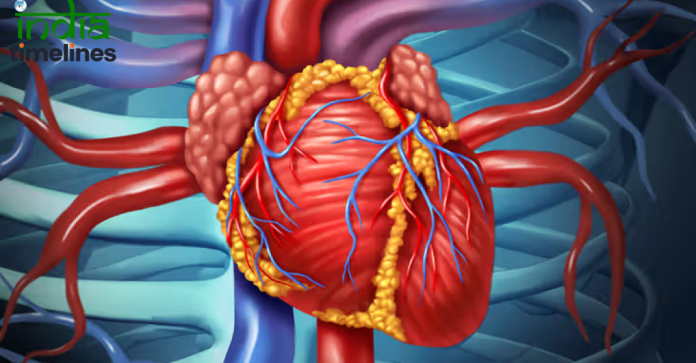
- Coronary Artery Disease: Blockages in the coronary arteries can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to angina (chest pain) or heart attacks. Surgery can help restore proper blood flow.
- Heart Valve Disease: When heart valves are damaged or dysfunctional, they may need repair or replacement to ensure proper blood flow through the heart.
- Heart Failure: Surgery can help improve heart function and symptoms in severe cases of heart failure.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some individuals are born with heart defects that require surgical correction.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms can sometimes be treated with surgical procedures.
- Aneurysms: Bulging sections of blood vessels or the heart wall may need surgical intervention to prevent rupture.
Types of Heart Surgery
Several types of heart surgery exist, each designed to address specific heart issues:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG):
- Purpose: To bypass blocked coronary arteries using grafts from other parts of the body.
- Procedure: The surgeon creates new pathways for blood to flow to the heart muscle, bypassing the blocked arteries.
- Heart Valve Repair or Replacement:
- Purpose: To fix or replace faulty heart valves.
- Procedure: Damaged valves are either repaired or replaced with artificial or biological valves.
- Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery:
- Purpose: To reduce recovery time and complications associated with traditional open-heart surgery.
- Procedure: Surgeons use small incisions and specialized instruments to perform the surgery.
- Heart Transplant:
- Purpose: To replace a severely damaged heart with a healthy donor heart.
- Procedure: The diseased heart is removed, and the donor heart is implanted.
- Arrhythmia Surgery:
- Purpose: To correct abnormal heart rhythms.
- Procedure: Techniques like maze surgery or ablation are used to disrupt the pathways causing the arrhythmia.
The Heart Surgery Process
Understanding the process involved in heart surgery can help patients and their families prepare:
- Pre-Surgery Preparation:
- Medical Evaluation: Comprehensive health assessment, including blood tests, imaging, and physical exams.
- Medications: Some medications may need to be adjusted or stopped before surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes: Recommendations may include quitting smoking, healthy eating, and exercise.
- The Day of Surgery:
- Hospital Admission: Arrive at the hospital and complete necessary paperwork.
- Pre-Operative Procedures: Change into a hospital gown, undergo last-minute tests, and meet with the surgical team.
- Anesthesia: Administered general anesthesia to ensure the patient is asleep and pain-free during the surgery.
- During Surgery:
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision to access the heart.
- Procedure: Depending on the type of surgery, the specific procedure is performed.
- Monitoring: Vital signs are continuously monitored throughout the surgery.
- Post-Surgery:
- Recovery Room: After surgery, patients are moved to a recovery room for close monitoring.
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU): Patients may spend time in the ICU for specialized care.
- Hospital Stay: The length of stay varies based on the surgery type and individual recovery.
Risks and Complications
Like any major surgery, heart surgery carries risks and potential complications, including:
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur, requiring antibiotics or additional treatment.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery may necessitate blood transfusions.
- Blood Clots: Can lead to complications like stroke or pulmonary embolism.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms may develop after surgery.
- Heart Attack: Although rare, a heart attack can occur during or after surgery.
- Lung Problems: Issues like pneumonia or difficulty breathing may arise.
- Kidney Problems: Surgery can impact kidney function in some patients.
Recovery After Heart Surgery
Recovery is a crucial phase that requires careful attention and adherence to medical advice:
- Immediate Post-Surgery Care:
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vital signs and heart function.
- Medications: Pain management and medications to prevent infection and blood clots.
- Hospital Discharge:
- Instructions: Detailed instructions on wound care, medications, and activity restrictions.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Schedule follow-up visits with the healthcare provider.
- At-Home Recovery:
- Rest: Ensure adequate rest and gradually increase physical activity as recommended.
- Diet: Follow a heart-healthy diet low in salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol.
- Exercise: Participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program or follow an exercise plan prescribed by the doctor.
- Long-Term Care:
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to the cardiologist to monitor heart health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintain a healthy lifestyle to support heart health, including managing stress, avoiding tobacco, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Tips for Patients and Families
Preparing for heart surgery and navigating the recovery process can be challenging. Here are some tips for patients and their families:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the specific type of heart surgery being performed and what to expect before, during, and after the procedure.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask the healthcare team questions about the surgery, risks, and recovery process.
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to all pre- and post-surgery instructions provided by the medical team to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Support System: Rely on family and friends for emotional support and practical assistance during recovery.
- Prepare Your Home: Set up a comfortable recovery area at home with easy access to essentials and minimize physical strain.
- Stay Positive: Maintain a positive outlook and focus on the long-term benefits of the surgery for improved heart health and quality of life.
Conclusion
Heart surgery is a significant medical intervention that can greatly improve quality of life and longevity for individuals with heart conditions. By understanding the reasons for surgery, types of procedures, the process involved, and the recovery journey, patients and their families can better prepare and navigate this challenging experience. With the right knowledge and support, heart surgery can be a stepping stone to a healthier and more fulfilling life.