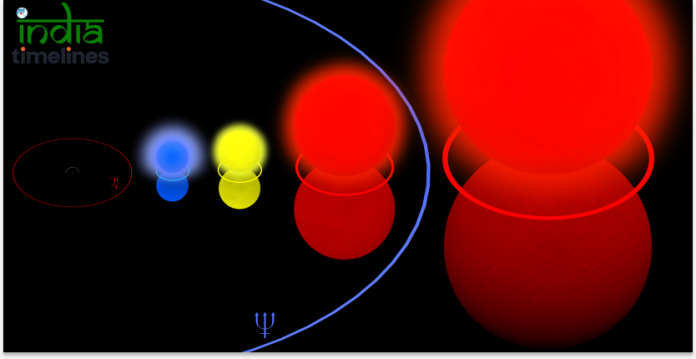
Supergiant stars are some of the most massive, luminous, and expansive objects in the universe. These stellar giants dwarf our Sun in size, brightness, and mass, and many of them are on the verge of reaching the end of their life cycle. Supergiants come in two categories: red and blue, depending on their temperature and color. Here’s a look at the top 10 largest supergiant stars in the universe based on their size, volume, and luminosity.
1. UY Scuti
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 1,700 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Scutum
- Facts: UY Scuti is the largest known star in terms of volume, although its mass is not as extreme as some others. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would extend beyond the orbit of Jupiter.
- Why It’s Unique: UY Scuti has the largest radius of any known star, making it the “king” of supergiants in size.
2. VY Canis Majoris
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Approximately 1,500 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Canis Major
- Facts: VY Canis Majoris was once considered the largest known star but has since been surpassed by UY Scuti. It is still one of the most massive and luminous red supergiants.
- Why It’s Unique: It has a strong stellar wind and is nearing the end of its life, likely to explode as a supernova.
3. Betelgeuse
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 1,000 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Orion
- Facts: Betelgeuse is one of the most famous stars in the sky. It is nearing the end of its life cycle and is expected to go supernova.
- Why It’s Unique: Known for its reddish color, Betelgeuse is one of the most visible stars to the naked eye.
4. Antares
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 850 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Scorpius
- Facts: Antares is the heart of the Scorpius constellation and is often referred to as the “rival of Mars” due to its red hue.
- Why It’s Unique: Antares is also a variable star, meaning its brightness fluctuates over time.
5. V354 Cephei
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Estimated to be around 2,100 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Cepheus
- Facts: V354 Cephei is an extraordinary red supergiant star that far surpasses the Sun in both size and luminosity.
- Why It’s Unique: This star is one of the most massive and luminous in the Cepheus constellation and is nearing the final stages of its lifecycle.
6. KW Sagittarii
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 1,500 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Sagittarius
- Facts: KW Sagittarii is one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way. It has an enormous radius and high luminosity.
- Why It’s Unique: Despite its size, its mass is not as extreme as some other stars, making it a prime example of a red supergiant.
7. Mu Cephei
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Approximately 1,650 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Cepheus
- Facts: Mu Cephei, also known as the “Herschel’s Garnet Star,” is one of the brightest stars in the Cepheus constellation.
- Why It’s Unique: This star has a deep red color, which is characteristic of its status as a red supergiant.
8. RW Cephei
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 1,535 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Cepheus
- Facts: RW Cephei is another large star in the Cepheus constellation. It has been observed to have significant variability in its brightness.
- Why It’s Unique: This star is one of the more massive red supergiants in the Milky Way galaxy.
9. IK Pegasi A
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Around 1,200 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Pegasus
- Facts: IK Pegasi A is part of a binary system. Its companion, IK Pegasi B, is a white dwarf, but IK Pegasi A is a supergiant star.
- Why It’s Unique: The unique binary system makes it an interesting object for astronomical studies.
10. UY Sagittarii
- Type: Red Supergiant
- Size: Approximately 1,500 times the radius of the Sun
- Location: Constellation Sagittarius
- Facts: UY Sagittarii is another impressive red supergiant that is massive in size. It is part of a smaller, more remote region of the galaxy.
- Why It’s Unique: Despite its size, it is not as well-known as some of the other supergiants but holds a prominent place among the largest stars.
Conclusion
Supergiant stars like UY Scuti and VY Canis Majoris represent the extremes of stellar size and luminosity. These stars are not only awe-inspiring in their vastness but also serve as important objects of study for understanding the life cycles of massive stars. Whether red or blue, these supergiants are destined for dramatic ends, either as supernovae or other catastrophic events that leave behind remnants like neutron stars or black holes. They are true cosmic giants, helping us understand the universe’s scale and complexity.
FAQs
- What is the difference between a red and blue supergiant?
- Red supergiants are cooler and larger in size compared to blue supergiants, which are hotter and have a more intense blue hue.
- Are all supergiant stars near the end of their life cycle?
- Yes, supergiant stars are typically in the later stages of stellar evolution, often preparing to explode as a supernova.
- Can a supergiant star become a black hole?
- Yes, if a supergiant star has sufficient mass, it can collapse under its own gravity to form a black hole after a supernova explosion.
- How can we observe supergiant stars?
- Supergiant stars can be observed using telescopes equipped with powerful optical, infrared, and sometimes radio capabilities due to their extreme luminosity.
- What happens to supergiant stars after they go supernova?
- After a supergiant star goes supernova, it may leave behind a neutron star or, if massive enough, collapse into a black hole.



































